Prețul cripto afișat este informativ și nu reprezintă prețul cripto live.
Graficul prețului monedei Bitcoin pentru ultimele 24 de ore arată variația prețului monedei Bitcoin (BTC) RON pe piața spot globală. Cumpărați Bitcoin RON pe platformă din contul dvs. Bitcoin la cel mai bun curs de schimb valutar Bitcoin.
Se încarcă datele graficului...
| Dată | Preț | Volum | MarketCap |
|---|
The evolution of Bitcoin price for the past 24 hours represents the price variation of the Bitcoin (BTC) crypto currency on the global spot market. Buy now Bitcoin with EUR on Tradesilvania from your Bitcoin account with EUR at the most advantageous exchange rate.
For anyone looking to understand market trends, a Bitcoin BTC Price Chart is an indispensable tool. These charts meticulously map the Bitcoin price history, allowing users to analyze its performance over any timeframe, from minute-by-minute fluctuations to its entire lifespan. Learning to interpret these charts is essential for both traders and long-term investors. They typically display price movements using candlesticks, which offer a rich data set for each period: the opening and closing prices, as well as the highest and lowest price reached.
Beneath the price action, you will almost always find a chart for the 24 hour trading volume. A high trading volume of Bitcoin signifies robust market interest and liquidity, often serving to confirm the strength of a price trend. For instance, a rising price accompanied by increasing volume is generally considered a more bullish and reliable indicator than a price increase on low volume. Analysts and experienced traders study these charts to identify patterns, gauge the collective psychology or market sentiment, and make more informed decisions about the future direction of the btc price.
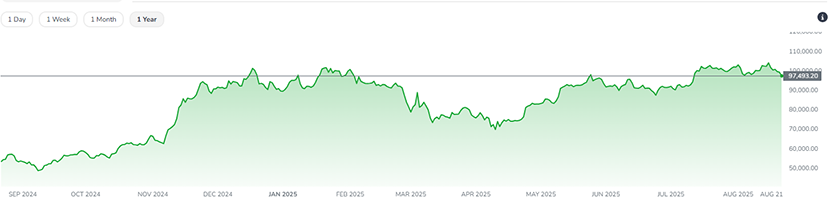
The Bitcoin price is the most visible and widely discussed aspect of this digital asset. It represents a global, real-time consensus on Bitcoin’s value, determined by the ceaseless interplay of supply and demand across hundreds of exchanges. Unlike the traditional stock market, which adheres to fixed opening and closing times, the crypto market operates 24/7. This constant activity means the price of Bitcoin is always in motion, reacting instantly to news, macroeconomic shifts, and changes in market sentiment from every corner of the world. This volatility is a defining characteristic of a nascent asset class. With a relative market cap still maturing, large trades can have a more pronounced effect on its price compared to established assets like gold. The USD price serves as the primary benchmark, but Bitcoin’s value is truly global, reflecting its worth against all other currencies and assets.
Bitcoin’s historical price is a remarkable story of volatility, resilience, and exponential growth. It’s a journey marked by distinct, cyclical bull and bear markets, often catalyzed by its pre-programmed halving events.
In the early days, Bitcoin was an obscure project with a value close to zero. The first significant real-world transaction, now famously commemorated as Bitcoin Pizza Day, occurred in 2010 when 10,000 bitcoins were used to purchase two pizzas, establishing an initial, albeit tiny, real-world valuation. The first major bull run followed the 2012 halving, catapulting the price to over $1,000 for the first time in 2013, which captured the world’s attention. After a prolonged bear market, the cycle repeated with greater force following the 2016 halving, leading to the monumental run-up that saw the price nearly touch $20,000 in late 2017.
The cycle following the May 2020 halving was amplified by a unique macroeconomic environment and surging institutional interest, when the Bitcoin price changed, which pushed the highest price paid for Bitcoin BTC to an unprecedented $68,000 in late 2021. The subsequent bear market was challenging, but it cleared the way for the next phase of maturation.
The most recent cycle, initiated by the April 2024 halving, has been fundamentally different. For the first time, the price achieved a new all-time high before the halving took place, a move largely attributed to the hugely successful launch of spot Bitcoin ETFs in the United States. This new financial product provided a regulated and accessible bridge for a massive wave of mainstream and institutional capital. The market’s upward trajectory continued through the end of 2024 and into the first quarter of 2025, setting a new record high well above $120,000. Now, as of August 2025, the market is in a necessary and extended consolidatory phase, having corrected significantly from its peak. This period of sideways price action and investor uncertainty is typical of mid-cycle pauses, as early investors take profits and the market seeks a stable foundation before its next major directional move.
In the vast and often tumultuous ocean of the crypto market, Bitcoin stands as the original titan, an innovation that has fundamentally challenged our understanding of money, ownership, and trust. Since its inception in 2009, Bitcoin has evolved from a niche experiment for cryptographers into a globally recognized digital asset with a market cap rivaling that of major corporations and national economies. Yet, despite its relative popularity, a deep understanding of what Bitcoin is and how does bitcoin work remains elusive for many. This guide aims to cut through the noise, journeying back to the foundations of Bitcoin to dissect its revolutionary technology, its unique economic principles, and the critical importance of security in a decentralized world.
To grasp the significance of Bitcoin, we must first understand the problem it was designed to solve. For decades, computer scientists sought to create a true form of digital cash, but they always stumbled on a critical hurdle: the double-spending problem. How could you prevent a user from spending the same digital token twice without a central authority, like a bank, to verify and settle every transaction? The answer was unveiled in 2008 with the publication of a document that would change the world.
At its core, Bitcoin is the world’s first successful decentralized cryptocurrency. It is a peer-to-peer electronic cash system that allows users to send and receive value directly with one another, anywhere in the world, without the need for a traditional financial intermediary. Unlike fiat currencies (like the US Dollar or the Euro), which are controlled by central banks, Bitcoin is governed by a set of rules—the Bitcoin protocol—and maintained by a distributed network of computers.
All Bitcoin transactions are recorded on a public, immutable ledger known as the Bitcoin blockchain. This blockchain acts as a universal book of accounts, providing a verifiable and transparent history of every transaction ever processed. It is this technological foundation that solves the double-spending problem, as the entire network can see and agree upon the history of transactions, making it impossible to spend the same funds twice. It is not just a payment system; it is a new form of property, a digital asset that can be held and secured by an individual without reliance on any third party.
The creation of Bitcoin is shrouded in a compelling mystery. In October 2008, a person or group operating under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto published the nine-page Bitcoin whitepaper, titled „Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System,” to a cryptography mailing list. This document elegantly laid out the framework for the system.
On January 3, 2009, Satoshi Nakamoto mined the very first block on the blockchain, known as the „Genesis Block.” Embedded within this block’s data was a now-famous headline from The Times newspaper: „The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks.” This message is widely interpreted as a commentary on the instability of the traditional financial system and a statement of purpose for Bitcoin as an alternative.
Satoshi continued to contribute to the project for about two years, collaborating with other developers online before gradually withdrawing from the community in 2011. The creator’s true identity has never been confirmed. This anonymity is now seen as one of Bitcoin’s greatest strengths. By not having a public founder or leader, the project avoided becoming dependent on a single individual and reinforced its core principle of decentralization. The former Bitcoin Foundation and numerous independent developers now contribute to maintaining and upgrading the protocol, guided by the global community of users and miners.
The magic of Bitcoin lies in its ingenious combination of cryptography, peer-to-peer networking, and game theory—a system known as blockchain technology.

Bitcoin’s uniqueness stems from a powerful set of characteristics that distinguish it from both traditional money and other crypto assets.
The process that secures the network and creates new coins is one of the most brilliant yet misunderstood aspects of the protocol. Bitcoin mining is the decentralized consensus mechanism that keeps the entire system honest and operational. It requires miners to perform a specific type of „work” to prove their legitimacy before they can add a new block of transactions to the blockchain.
This „work” involves using powerful computers to repeatedly run a cryptographic hashing function (SHA-256) on the block’s data, plus a random number called a „nonce.” The goal is to find a hash value that is below a certain target set by the network. Because the output of a hash function is unpredictable, this is essentially a lottery. The miner who finds a valid hash first wins the right to add their block to the chain and claims the reward. This reward consists of newly created bitcoins (the „block subsidy”) and all the transaction fees from the transactions included in the block. This entire process is what many simply call Bitcoin work.
The network automatically adjusts the difficulty of this puzzle approximately every two weeks to ensure that, on average, a new block is found every 10 minutes, regardless of how many miners are competing. This ensures a predictable issuance schedule for new coins. While essential for security, it is important to note that Bitcoin’s energy consumption is a significant topic of debate.
One of the most profound features of Bitcoin’s monetary policy is the Bitcoin halving. Coded into the protocol from the very beginning, this event reduces the block subsidy reward given to miners by 50%. It occurs automatically every 210,000 blocks, which translates to roughly once every four years.
The halving directly cuts the inflation rate of Bitcoin in half and is a powerful mechanism for enforcing its scarcity. Each halving event serves as a stark reminder of the asset’s diminishing new supply, which has historically had a significant impact on market sentiment and the price of Bitcoin.
While the network itself is robust, the security of an individual’s holdings is a matter of personal responsibility. The crypto mantra, „Not your keys, not your coins,” is a critical principle to understand. If you entrust your crypto assets to a third-party exchange or custodian, you are trusting them not to be hacked, go bankrupt, or restrict your access. To truly hold Bitcoin is to control your own private keys.
The private key is the single piece of information that proves ownership and allows you to sign transactions. If you lose it, your funds are lost forever. If someone else gets it, they can steal your funds. Therefore, managing this key is the most important aspect of Bitcoin security.
Cryptocurrency wallets are the tools used to manage these keys. They come in two main categories:
Securing your Bitcoin is a multi-layered process. It involves choosing the right wallet for your needs, backing up your recovery phrase (a list of words that can restore your wallet), using strong, unique passwords, and being perpetually vigilant against phishing scams and fraudulent schemes. In the world of Bitcoin, you are your own bank—a responsibility that brings with it unparalleled freedom but also demands diligence.
The question of why Bitcoin’s price is so volatile is complex, with a multitude of interconnected factors at play.
Cumpără Bitcoin (BTC) instantaneu în contul tău Tradesilvania
Cat costa un Bitcoin?
Platforma noastră îți permite să-ți reîncarci contul cripto cu EUR și RON instantaneu și cu costuri reduse. Folosește transferul IBAN pentru o reîncărcare cu comision 0%.
BTC – RON – Transfer bancar IBAN
BTC – EUR – Transfer IBAN (0%)
BTC – Visa – Instant EUR
BTC – Mastercard – Instant EUR
BTC – Reîncărcare instantanee cu plată automată RON
BTC – RON un-doi – Reîncărcare instantanee
BTC – RON Qiwi (Start Pay) – Reîncărcare instantanee
BTC – EUR Skrill – Reîncărcare instantanee
BTC – EUR Neteller – Reîncărcare instantanee